Important process: blood glucose monitoring benefits & how to
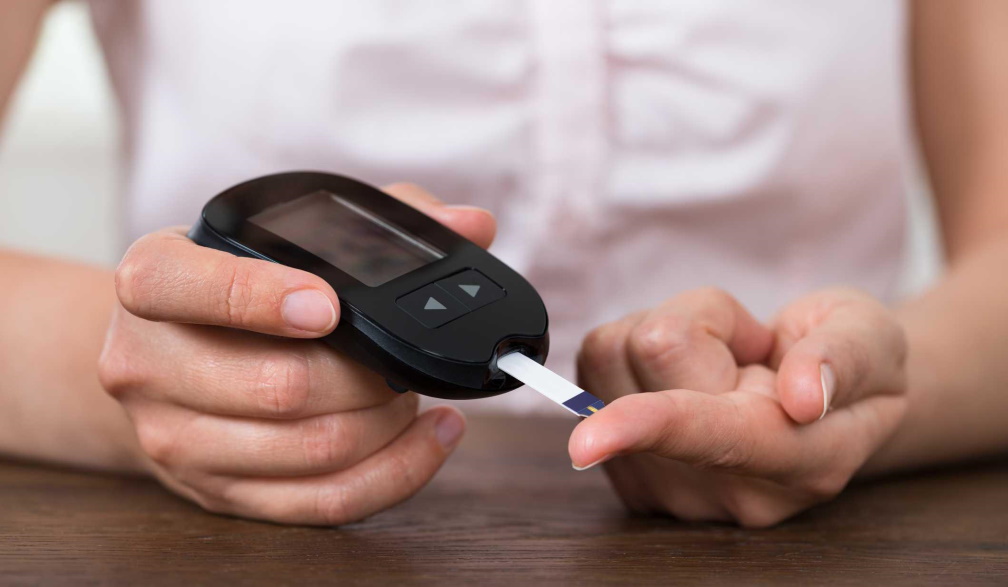

Consistent blood glucose monitoring is important for you if you suffer from diabetes. It is one of the optimal ways you can better understand your condition, especially when it comes to making decisions about diet, exercise and medication dosage, as understanding your blood glucose levels can affect these decisions and help your doctor.
By routinely checking your blood glucose levels, you will have a sound idea of whether your blood sugar is too low or high, both of which can be detrimental to your health.
Your doctor or healthcare team will calculate the target range for your blood glucose based upon your age, overall health, diabetes type and a host of other factors. It’s imperative to keep your blood glucose levels within your target range as going outside of this range can be detrimental to your health.
Blood glucose monitors are one of the most handy medical technologies for diabetics, so let’s take a closer look at how to use them:
Before you use your blood glucose monitor
Before you conduct a blood glucose reading, you have to ensure that you have:
-
A finger-stick device like a lancet that can prick your finger;
-
An alcohol swab for sterilising the puncture site post-prick
-
A blood glucose monitor
-
A bandage in the case of continued bleeding from the puncture site
What’s more, you may need to adjust your meal schedule or time the test around your meal, depending on your doctor’s advice and what kind of test you are taking.
How to undertake blood glucose monitoring
Before conducting the test, ensure your hands are thoroughly washed to avoid infection at the puncture site. If you opt for alcohol wipes as opposed to washing, allow the puncture site to dry before undertaking the test.
Next, insert a testing strip into the meter. Prick your finger with your lancet to allow a small drop of blood to come out of the site. It is a good idea to prick the side of your finger as opposed to the tip as pricking the tip could be unpleasant.
You then place the blood onto the test strip that is inside the meter. Your monitor will evaluate the blood and provide you with a blood glucose reading on the display in real time.
Finger pricks don’t typically require any extra medical attention, but if bleeding persists then it may be a good idea. You should follow all instructions that come with your glucose device to ensure you achieve the most accurate results possible.
For type 1 diabetics, you might want to test your blood glucose numerous times a day (four or more is a good place to start). This is typically done before and after exercise and meals, but undertaken more regularly if you are unwell.
For type 2 diabetics, your doctor will tell you when and how regularly you should conduct a blood glucose test.
Understanding your blood glucose results
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology recommends, as a guideline, that you keep pre meal and fasting glucose values at 80-130 and post-prandial <180. Furthermore, they recommend that you maintain two-hour post-meal reading values at 140 mg/dl.
But these are just general health guidelines that differ from person to person. You should always consult your doctor when it comes to deciding your target levels.
Regular blood glucose monitoring is a vital tool to help you be more comfortable with and have control of your diabetes. Through the routine identifying and recording of blood sugar changes, you will have a better understanding of how to handle stress, exercise, meals and other factors that impact your diabetes.